CATALYTIC PROPERTIES OF F-CENTRES AT THE MgO SURFACE
R. Orlando*, R. Millini**, G. Perego** and R. Dovesi*
* Dipartimento di Chimica IFM, Università di Torino,
via Giuria 5, I-10125 Torino, Italy
** Eniricerche S.p.A. Phys. Chem. Dept.
via Maritano 26, I-20097 San Donato Milanese,Italy
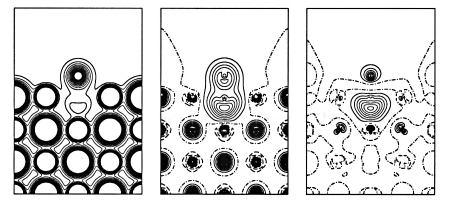
Anion vacancies in magnesium oxide are claimed to be involved, as active sites, in the catalytic abstraction of hydrogen from methane [1]. The electronic structure and the energetics for the formation of F-centres in MgO and hydrogen adsorption thereon (figure below) are calculated in an infinitely periodic (001) slab with the ab-initio Hartree-Fock approximation, implemented in the CRYSTAL program [2]. Three-layer slabs comprising up to 16 MgO-units/layer are shown to be an adequate model for the description of the surface and catalytic properties of the substrate. Different coordinations of ions at the surface, like in the formation of steps, are also considered, as well as the possible coupling of F-centres with Li+ substituting dopants, which may be present in the Li-doped MgO catalyst [3].

References
[1] W.C. Mackrodt in Computed Simulations of Solids, Lecture Notes in Physics n. 166, Springer Verlag 1982.
[2] R. Dovesi, V.R. Saunders and C. Roetti, CRYSTAL95 User's Manual, Gruppo di Chimica Teorica, Università di Torino, Torino (1995).
[3] D.J. Driscoll, W. Martir, J. Wang and J.H. Lunsford, JACS. 107 (1985) 58.